3 Rules for Digital Health in a Digital Society

Digital society has already arrived for billions of people, but the implementation of digital health is just beginning.
We’re now starting to understand which digital solutions can help solve healthcare issues, like tracking digital biomarkers for example. We’re also realizing that our digital society can create new healthcare problems. Brain hacking?
If we ignore the critical gap between digital society and digital health, it will only grow over time. The ideas below put an emphasis on being proactive.
1. Prevent upstream digital health problems.
It took time, but we’re making progress in dealing with upstream problems such tobacco, environmental toxins, and food safety. There are also far-reaching challenges upstream when it comes to digital society.
This includes health issues related to social networks, digital devices, and artificial intelligence. When the business models of these industries conflict with healthcare outcomes of society, the business models will win.
While there are still not enough research studies, the ones that have been completed are coming up with some disturbing results.
“All screen activities are linked to less happiness, and all nonscreen activities are linked to more happiness. Eighth-graders who spend 10 or more hours a week on social media are 56 percent more likely to say they’re unhappy than those who devote less time to social media.” — Jean M. Twenge
The above analysis is related to The Monitoring the Future survey, designed to be nationally representative in the US, with more than 1,000 questions for 12th-graders every year since 1975 and eighth graders since 1991.
One of the additional challenges with the digital world is that we should expect legal rules to be consistently behind the curve. Regulators are currently not equipped with the right skills, incentives, and resources to keep up with changes in digital technology.
Thus it is up to the private sector, both consumers and businesses, to be proactive. Tech employees are starting non-profits focused on identifying potential harm of digital platforms. Business leaders are taking a stand about digital advertising. Investors are communicating that social purpose must be tied to profits. We need more of all of the above — being passive is not a solution.
2. Avoid private sector monopolies for public goods.
Healthcare companies save millions of lives every year. That shouldn’t stop us from identifying clear evidence of business model misalignment which can lead to adverse health outcomes, even death. This challenge already exists in healthcare, and it is absolutely relevant for digital health.
The history of patent law describes a very complicated balance between stakeholders. Most people want innovation. There is disagreement on the right mix of incentives.
As part of this debate, it’s always important to check on the final results. The story of rising insulin prices in the US is one example. A quick glance at the chart below makes it clear that the current mix of incentives is not leading to desired outcomes. The system is being gamed.
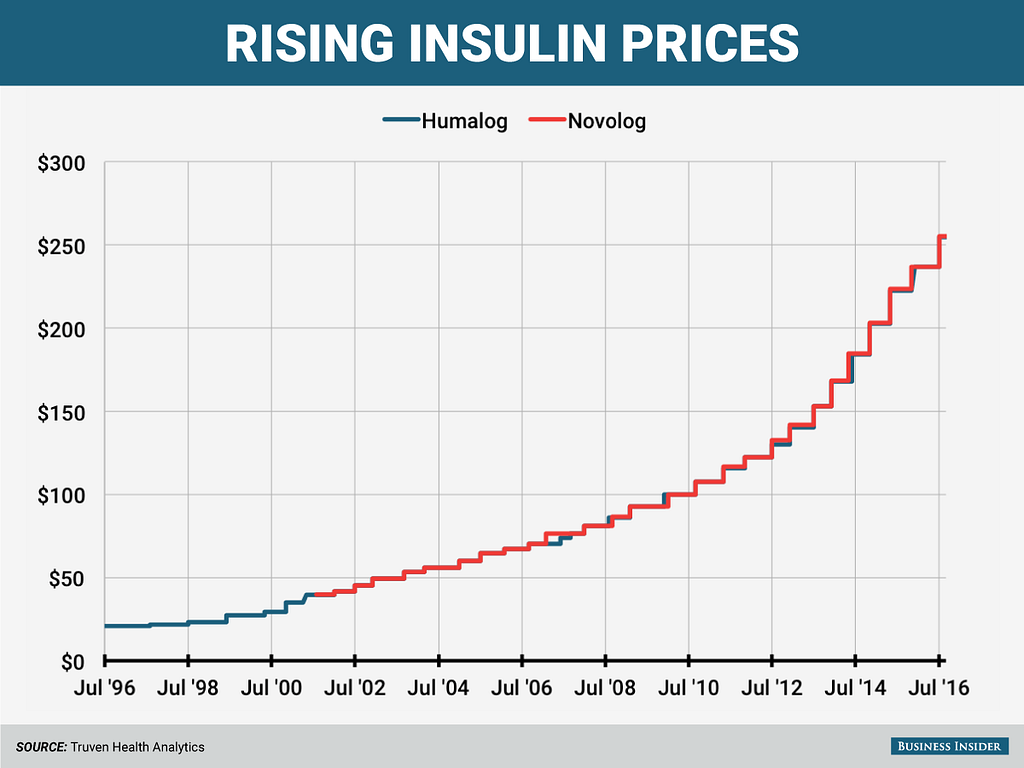
It’s easy to blame the companies, and they are absolutely part of the problem. They are also responding to the incentives of the system.
With digital health, this challenge becomes even more relevant because digital health products and services should be highly deflationary over time. If we see rising prices for digital health services in the future, that would be a massive failure of incentives.
A single private company owning a patent on a multi-billion dollar revenue life-saving treatment is a private sector monopoly resulting in less competition. When the state uses its powers of coercion to enforce this patent, it makes a value judgement that society is better off in having a private sector monopoly instead of competition. Given the long history of abuse by private sector monopolies across a wide variety of businesses, we typically expect a high level of price regulation to accompany monopoly power, and healthcare should not be exempt.
Many life-saving drugs were initially supported through government funded research. The pricing of these drugs has a massive impact on the healthcare outcomes. And we know that a monopoly will naturally lead to overpricing precisely because of a lack of competition. So at the very least, the burden of proof should be on the company to maintain a monopoly, not society. Also, it would be incompetent for society to outsource the pricing of drugs to monopoly holders of patents.
This logic applies to the owners of digital health patents, except with even more potential for misalignment. The burden of proof for digital health patents should be extremely high, not low.
Moreover, once a digital health patent is granted, that monopoly pricing power needs to be regulated. In the digital world, it’s not enough to expect modest price inflation. We know that competition in the digital world results in severe price deflation and this should be the benchmark for any price regulation of digital health monopolies.
3. Ensure user friendly data portability.
Forgetting about distribution channels is easy. In the digital world, however, these channels have direct relationships with customers, and importantly also customer data. Digital super-aggregators enjoy some of the most influential market power ever witnessed in the history of business.
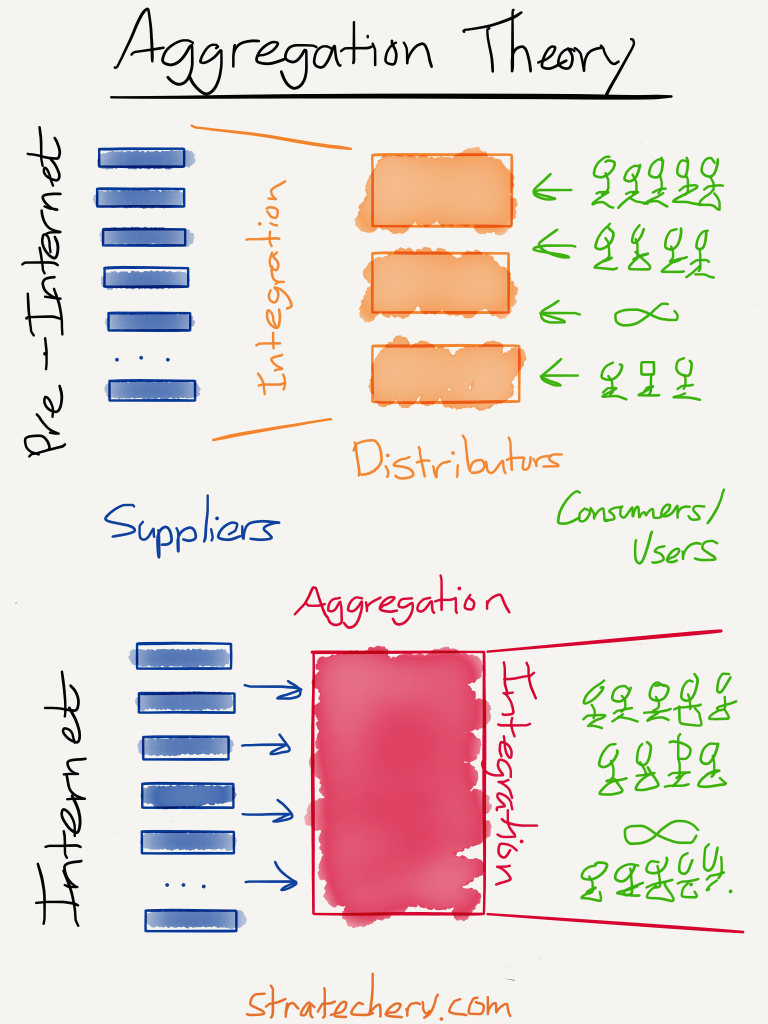
There are already problems in healthcare with the market power enjoyed by distribution channels. The potential for abuse of power in digital health distribution is even more significant. It’s mostly a good thing that companies like Amazon are entering healthcare aggressively. But let’s not assume that the company and others will be immune from increasing market power.
Specifically, we need to have more clarity about healthcare data portability. It’s tempting to use the word healthcare data ownership, but the topic is not that simple. There is a difference between ownership, control, and privacy. While the infrastructure and nuances of those issues will need time to sort out, the most obvious starting point is data portability.
Patients should have the right to access and transfer the data being gathered about their health. This will become even more important in the future as the amount of passively collected digital healthcare data will increase exponentially. If an algorithm is analyzing your health from a video camera recording, does the algorithm need your permission? Would you want the right to access that data output if you choose?
Regulators will be way behind the curve on this issue. In addition, most users of healthcare are likely to choose convenience over control. At the very least, we need to ensure that there is an option for user-friendly digital data portability if someone decides to switch health providers.
Moving forward
When it comes to digital healthcare, we can’t wave a magic wand and say “let the government deal with it, it’s not my problem.”
It would also be irresponsible to take the view that large companies will solve these challenges on their own.
All stakeholders have to work together for meaningful progress in digital healthcare. It’s part of Capitalism 2.0 where we all have a role as patients, healthcare specialists, caregivers, employees, public servants, non-profit leaders, business executives, startup founders, social impact innovators, and investors.
3 Rules for Digital Health in a Digital Society was originally published in Fusion by Fresco Capital on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.